
Ohayon MM, Carskadon MA, Guilleminault C, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the pharmacologic treatment of chronic insomnia in adults: an American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline. Physician and patient determinants of pharmacologic treatment of sleep difficulties in outpatient settings in the United States. 2005 1:e477–9.īalkrishnan R, Rasu R, Rajagopalan R. The natural history of insomnia: focus on prevalence and incidence of acute insomnia. A survey of sleep habits and sleeping difficulties in an elderly Swedish population. An epidemiological study on insomnia in an elderly Thai population. Sleep problems in Chinese elderly in Hong Kong. Sleep complaints in community- dwelling older persons: prevalence, associated factors, and reported causes. Insomnia in the elderly: prevalence, gender differences and relationships with morbidity and mortality. 1995 162:22–4.īrabbins CJ, Dewey ME, Copeland JRM, et al. Insomnia in the elderly: its prevalence and correlates in the general population. Relationship between daytime sleepiness and cognitive functioning in an elderly population. Incidence and remission of insomnia among elderly adults: an epidemiologic study of 6800 persons over three years. Sleep complaints among elderly persons: an epidemiologic study of three communities. Clinical guideline for the evaluation and chronic management of chronic insomnia in adults. Schutte-Rodin S, Broch L, Buysse D, et al. New developments for treating sleep disorders. Histamine receptor inverse agonists (APD-125, eplivanserin, and LY2624803) improve slow-wave sleep but, for various reasons, the drug companies withdrew their products.į.
Piromelatine may improve sleep maintenance. Phase II studies of dual orexin receptor antagonists (almorexant, lemborexant, and filorexant) have shown some improvement in sleep maintenance and sleep continuity. Valerian is relatively safe but has equivocal benefits on sleep quality. Tryptophan decreases sleep onset in adults, but data in the elderly are not available. Melatonin slightly improves sleep onset and sleep duration, but product quality and efficacy may vary. Non-FDA-approved hypnotic agents that are commonly used include melatonin, diphenhydramine, tryptophan, and valerian, despite limited data on benefits and harms.

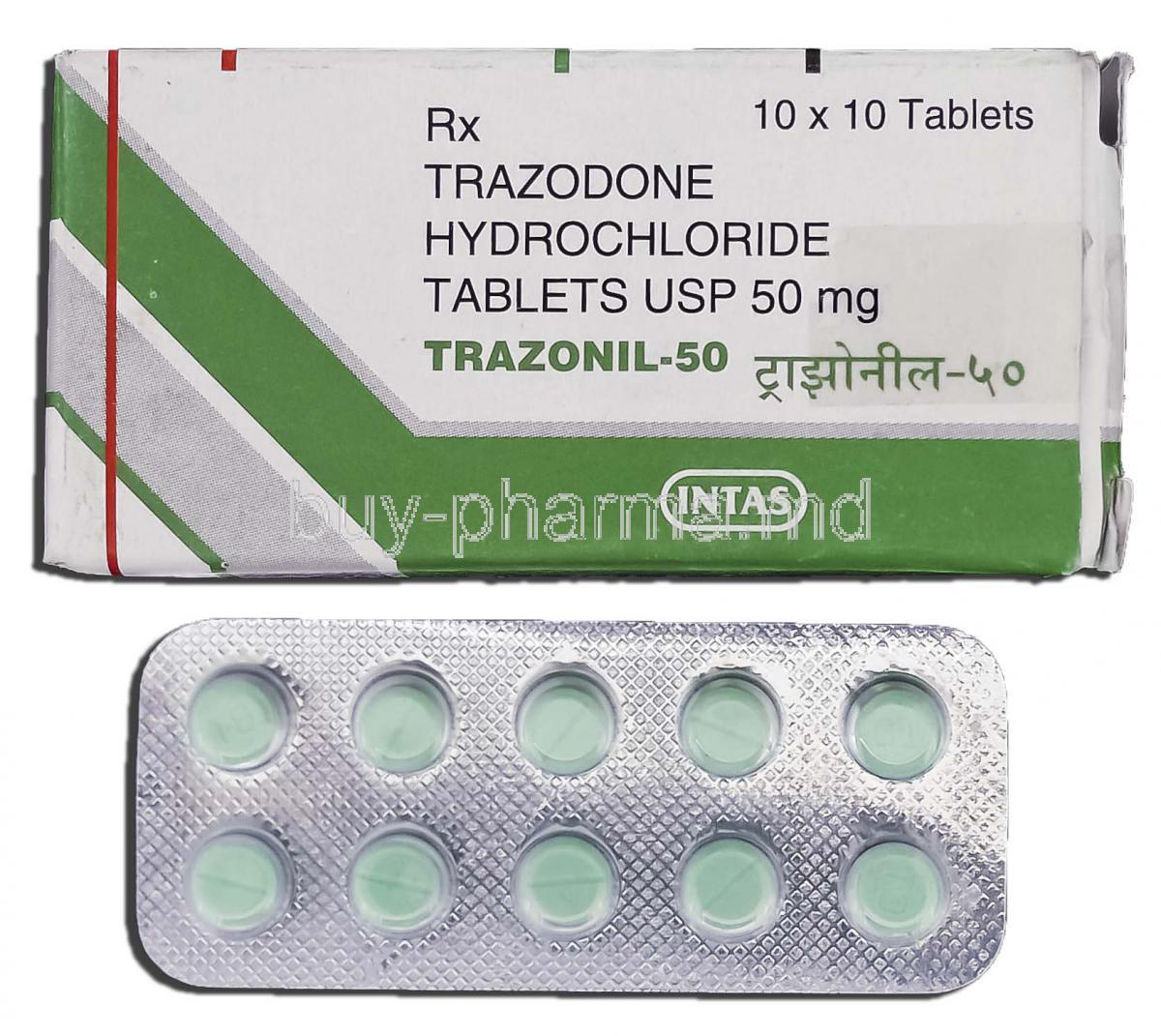
Tiagabine, sometimes used off-label for insomnia, is not effective and should not be utilized. Trazodone, a commonly used off-label drug for insomnia, improves sleep quality and sleep continuity but carries significant risks. Benzodiazepines should not be used routinely. Low-dose zolpidem sublingual tablets or zaleplon can alleviate middle-of-the-night awakenings. Eszopiclone or zolpidem extended release can be utilized for both sleep onset and sleep maintenance.

Suvorexant or low-dose doxepin can improve sleep maintenance. Ramelteon or short-acting Z-drugs can treat sleep-onset insomnia. The choice of a hypnotic agent in the elderly is symptom-based. We review the indications, dosing, efficacy, benefits, and harms of these drugs in the elderly, and discuss data on drugs that are commonly used off-label to treat insomnia, and those that are in clinical development. This review focuses on Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drugs for insomnia, including suvorexant, low-dose doxepin, Z-drugs (eszopiclone, zolpidem, zaleplon), benzodiazepines (triazolam, temazepam), and ramelteon. Current drugs for insomnia fall into different classes: orexin agonists, histamine receptor antagonists, non-benzodiazepine gamma aminobutyric acid receptor agonists, and benzodiazepines. Pharmacotherapy plays an adjunctive role when insomnia symptoms persist or when patients are unable to pursue cognitive behavioral therapies. Various specialty societies view psychological/behavioral therapies as the initial treatment intervention. The main modalities in the treatment of insomnia in the elderly are psychological/behavioral therapies, pharmacological treatment, or a combination of both. Chronic insomnia burdens society with billions of dollars in direct and indirect costs of care.

Chronic insomnia affects 57% of the elderly in the United States, with impairment of quality of life, function, and health.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
